
According to the National Alliance for Mental Health, 19% of adults in the United States have an anxiety disorder. That’s a whole lot of anxiety! That doesn’t even consider those who have a small bout of panic here and there. But, can anxiety and/or stress cause blurred vision?
If you are a parent, like myself, it’s almost a given stress will get the best of you occasionally…..or more than occasionally.
Do you ever suddenly find yourself having blurry vision during times of stress or anxiety? I know this can be concerning….from personal experience. I call it “walking around in my cloud of anxiousness.” Seriously, it can be so strange….like being in a dream.
So….is that blur caused by anxiety and stress? The short answer is that it COULD be.
Let me explain:
- Stress and panic trigger the “flight or fight” response. Pressure builds on the eyes resulting in many eye issues including blurred vision.
- Extreme stress and anxiety can make you feel dizzy resulting in blurry vision.
Before you conclude that your blurred vision is caused by anxiety and/or stress, there is other information that is important to know. So…..let’s jump right in!
What is Anxiety?
I am no stranger to anxiety…… To me, it is not being able to take anything but shallow breaths. It’s a feeling of helplessness that comes and goes sometimes without any reason. It’s my heart skipping around in my chest or getting irritated easily.
To others, it may be a different experience.
Symptoms of Anxiety
The most common anxiety symptoms are:
- Feeling restless
- Experiencing excessive worry
- Being irritable
- Having sleep difficulties
- Experiencing unexplained aches and pains
- Being fatigued
- Having concentration difficulties
- Experiencing heart palpitations
- Having chest pain
Anxiety Disorders
Generalized Anxiety (GAD)
- When anxiety and worry interfere with daily activities.
- Anxiety and worry that is difficult to control.
- Worry is out of proportion for the situation.
- Tend to expect disaster.
Panic Disorder
- Having frequent, unexpected panic attacks.
- Sense of losing control.
- Having overwhelming fear without a cause for the fear.
Phobias
- An overwhelming and unreasonable fear of objects or situations that pose little real danger but provoke anxiety and avoidance (Mayo Clinic).

Social Anxiety Disorder
- When anxiety occurs in certain social situations due to fear of being judged, rejected, or embarrassed.
Separation Anxiety Disorder (SAD)
- Excessive anxiety or worry over separation from or thought of separation from an attached figure such as a parent.
- Usually occurs in babies starting around 8 months old and disappearing by 2 years old.
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- Having a chronic (long-lasting) state of anxiety.
- Having frequent, irrational, disturbing thoughts (obsessions) that cause anxiety.
- Having an uncontrollable urge to repeat certain behaviors (compulsions).
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Develops because of exposure to or witnessing a traumatic, stressful event.
- “Fight or flight” response is triggered when no longer necessary.
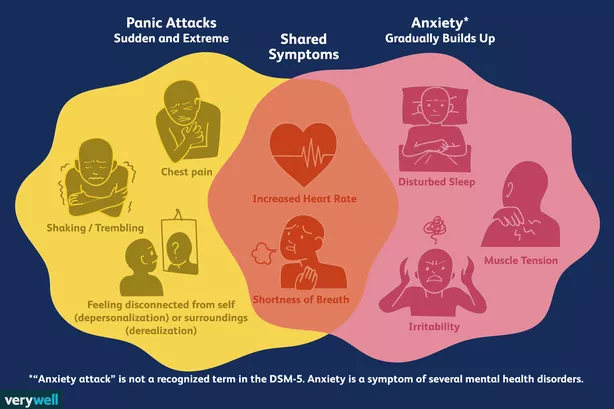
Anxiety Attacks
So what are anxiety attacks, also known as panic attacks? How is it different than generalized anxiety?
An anxiety attack is an episode of intense fear, panic, or worry. Whereas, generalized anxiety is not episodic and lacks the same amount of intensity.
These attacks are high levels of anxiety that are often linked to a trigger. For example, a person who grew up in an abusive household may have a panic attack triggered by yelling, screaming, or crying. This can make it difficult for parents because children often do all these things while they are learning emotion regulation.
Common Causes of Anxiety
There isn’t just one common cause that triggers anxiety. What we do know is that both environmental stressors and genetics are risk factors for developing anxiety. However, there are some common causes.
- Daily life stressors from work or school
- Past or childhood experiences
- Chronic stress (relationships, financial)
- Stress from emotional trauma
- Genetics
- Brain chemistry
- Medication side effects
- Caffeine
- Physical health conditions (thyroid problems, heart arrhythmia)
“Fight or Flight” Response
To fully understand anxiety, it’s also important to be familiar with the “fight or flight” response.
The experience of fear and anxiety are similar. With both fear and anxiety, a person may perceive themselves as being in danger. However, with anxiety there is no actual danger, the person just thinks there is.
When a person feels threatened or in danger, the “fight or flight” response is activated. As the stress levels increase, cortisol levels (the stress hormone) increase. This happens to protect the person. Here are the different ways the body changes during this response:
- Cortisol “the stress hormone” is released by the adrenal glands into the bloodstream.
- An increase in sweating to prevent the body from overheating.
- Pupils widen to enable better vision.
- Decreased activity in the digestive system.
- Increased tension in muscles.
- Increase in heart rate and strength of beat so that blood gets pumped around the body faster delivering oxygen to vital parts of the body.
- Blood flows away from parts of the body it is not needed.
- Breathing changes to provide extra oxygen to vital tissues in the body.
Risk Factors of Anxiety
- Experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event.
- Extreme stress, including stress due to illness.
- Having a certain personality type.
- Having another mental health disorder such as depression.
- Having others in your family with anxiety.
- Certain drugs and alcohol can increase anxiety.
- Brain structure
Treatment Options for Anxiety
Anxiety can range from mildly uncomfortable to debilitating. The effects of stress from anxiety can impact your daily life in a significant way. The good news is that there are many different medications and other treatments available to help.
- Psychotherapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)– A treatment that usually involves changing thinking patterns.
- Psychological Counseling
- Biofeedback– A technique that includes using sensors and other ways to receive information from your body to learn how to control some of your body’s functions.
- Self-treatment
- Managing triggers
- Relaxation and mindfulness
- Social support
- Increasing quality of sleep
- Reducing substances such as alcohol and nicotine
- Increasing exercise
- Anti-Anxiety Medications
- Anti-depressants
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI)
- Serotonin and noradrenaline Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRI)
- Anti-convulsants
- Benzodiazepines (sedatives)
- Anti-depressants
Alternative Treatments for Anxiety

- Esketamine nose spray
- Eye Movement Therapy (EMDR)– Involves moving your eyes a certain way while you process certain events.
- Robots that provide emotional support (Woebot)
- Nutritional Supplements
- Vitamin B12
- Chamomile
- Passionflower
- L-theanine
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Ashwagandha
- Magnesium
- Vitamin D
- CBD products
- Essential Oils
- Valerian
- Lavender
- Bergamot
- Jasmine
- Frankincense
- Ylang Ylang
- Vetiver
- Holy Basil
What is Blurred Vision?
Blurred vision occurs when there are any problems with the cornea, optic nerve, or retina of the eye.
We’ve all experienced eye problems, specifically blurred visual symptoms. Sometimes it happens when we’ve been sitting in the dark for a long time and then turn on a light. It takes our eyes a few seconds to adjust. Have you ever taken daytime cold medicine? That can cause vision changes that make everything a little blurry too!

Symptoms of Blurred Vision
- Vision is not sharp
- Difficult to see the fine details of an image
- Images appear as out of focus
- Double vision
Eye Conditions (and other medical conditions that cause blurred vision problems)
- Stroke
- Optic Neuropathy– Damage to the optic nerve as a result of a change in blood flow.
- Retinal detachment
- Concussion
- Brain tumor
- Cataracts
- Closed-angle glaucoma– When the pressure in your eye becomes too high.
- Wet Macular Degeneration– Chronic eye disorder that causes blurred vision or a blind spot in your visual field.
- Endophthalmitis– An infection of the tissues or fluids inside the eyeball.
- Diabetic Retinopathy– Diabetes complication that causes damage to blood vessels on the light-sensitive tissue on the back of the retina.
- Eye infections such as Conjunctivitis
- Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA)- Inflammatory disease affecting the large blood vessels of the scalp, arm, and neck.
- Retinal Migraine
- Eye-strain
- Hyphema– Collection of blood in the anterior chamber of the eye.
- Binocular Vision Dysfunction (BVD)– Condition where the line of sight from one eye is out of line with the sight of the other eye.
- Dry eye syndrome– A common condition where your tears are not able to provide enough lubrication for your eyes.
Common Causes of Blurred Vision
- Nearsightedness (Myopia)
- Farsightedness (hyperopia)
- Refractive Errors- When the curve of the eye interferes with the light focusing on the retina.
- Cataracts
- Trauma to the eye
- Migraines
- Optic Neuritis- Inflammation of the optic nerve.
- Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Mental stress
- Dry eyes
- Low blood sugar
Blurred Vision Risk Factors
- Family history
- Exposure to sunlight and UV rays
- Age
- Drugs such as antidepressants, diuretics, and antihistamines
- Smoking
- Alcoholism
- Trauma to the eye
Blurred Vision Treatment
There are many causes of blurred vision and that is why there isn’t one fix-all treatment. To find a solution for blurred vision, the cause needs to be determined. The best way to do this is to make an appointment with your eye doctor to get an eye exam.
Here are some common treatments for blurred vision:
Natural Treatments
- Rest using the 20-20-20 rule to reduce eye strain
- Lubrication
- Eye Yoga
- Getting more Omega-3 and Vitamin A
- Quit smoking
- Protect your eyes from UV rays by wearing sunglass
- Make sure your contacts are clean
Other Treatments
- Lasik eye surgery
- Cataract surgery
- Artificial drops and ointments
- Eyeglasses
- Laser surgery
To Sum it Up
I shared a lot of information on blurred vision and anxiety in this article. The main takeaway is that anxiety can cause blurred vision. Blurry vision can also be caused by several other medical conditions. That’s why you should err on the side of caution and get it checked out by a professional if you are not sure.




I was very happy to find this great site. I want to to thank you for your time due to this fantastic read!! I definitely savored every little bit of it and I have you saved to fav to see new stuff in your web site.
Thank you for your feedback! I’m so glad you enjoyed my site!